Tech Trends to Expect in 2022
- walkerinthecloud
- Jan 22, 2022
- 8 min read

In 2020, many technological advancements came to a standstill as the world braced for the unknown and the markets took a dive. However, the pandemic accelerated growth exponentially in some industries, like pharmaceuticals, developing Covid-19 rapid tests and vaccines. It also drove the widespread adoption of collaboration tools and migration from legacy data centers to cloud services, all to support remote work.
In 2021 we saw a bit of normalcy, especially as companies tried to get back to business as usual, despite having some or most of their workforce still remote. There were also a couple of firsts for the history books, including the launch of space's largest telescope, James Webb, promising a glimpse into the history of our creation. We also saw the widespread use of the world's first RNA genetic modifying vaccine. We saw the first all-civilian spaceflight, which paves the way for the commercial space age of tourism for the everyday person (or everyday multi-millionaire, at least).
We can expect many of last year’s achievements to shape 2022 while the overall development of technology takes its rightful place in society. This includes investing in cryptocurrency made so easy your grandparents can buy Bitcoin. It includes the realization of the benefits of virtual reality (VR) in the boardroom and the beginning of a significant public acceptance of Web 3.0 and dollars in your wallet every time someone collects or uses your personal data.
Below are the top 10 biggest technology trends to look out for in 2022. Many are not new but will see greater discussion and deeper understanding in the coming years.
Launch of the James Webb Telescope and the Unanswered Birth of the Universe.
While the James Webb Telescope was technically launched on December 25, 2021, it will not reach its destination until the end of January. Unfortunately, the public may not see its first images until May of this year.
The James Webb Telescope is the largest telescope NASA has ever launched into space. It is 100 times more powerful than the famous Hubble Telescope launched in 1990. The Hubble gave us beautiful images of our universe, including the pictures below of the Eagle Nebula, a birthplace of new stars, and photos of millions of galaxies, millions of lightyears away. The James Webb will allow us to see even further into our history and hopefully discover the first stars and galaxies of the universe, giving us answers as to how it exists.
The below image to the left shows the Eagle Nebula taken by the Hubble Telescope Scope. The image on the right is an artist's rendition of what the James Webb Telescope could see in the same area.
The Next Era of Hacking: DNA, RNA, and Genetic Code Splicing
Since the 1960s, the term “hacking” has generally referred to data hacking within computers or computer networks such as the cloud. When we think of hacking, we think of Edward Snowden or groups like Anonymous, putting the world's deepest secrets out on the dark web. But there is a much more dangerous version of hacking on the rise: genetic modification of our DNA. Although if misused and unregulated, it has the potential to become a dystopian nightmare like Brave New World or a world where the rich can modify their offspring to be better looking, more intelligent, or capable of superhuman athleticism.
In a utopian world and with our current capabilities, genetic engineering also can cure diseases like Sickle Cell or Huntington’s disease by modifying human RNA structure. RNA is similar to DNA, but has different functions. For example, DNA stores the genetic information of a cell, and the RNA acts like a messenger, perfect for splicing and hacking. The discovery, by the Nobel Prize winner Jennifer Doudna and her team, of a means to splice RNA had a significant impact on the development of tests and vaccines for Covid-19.
In Walter Isaacson's new book, The Code Breaker, about the discovery of RNA splicing and the academic life of Doudna, he states that the past half-century has been a digital age based on computing and the birth of the internet, but we are now entering a life-science revolution. Children who study digital coding will be joined by those who study the code of life in what he terms "evolution-hacking."

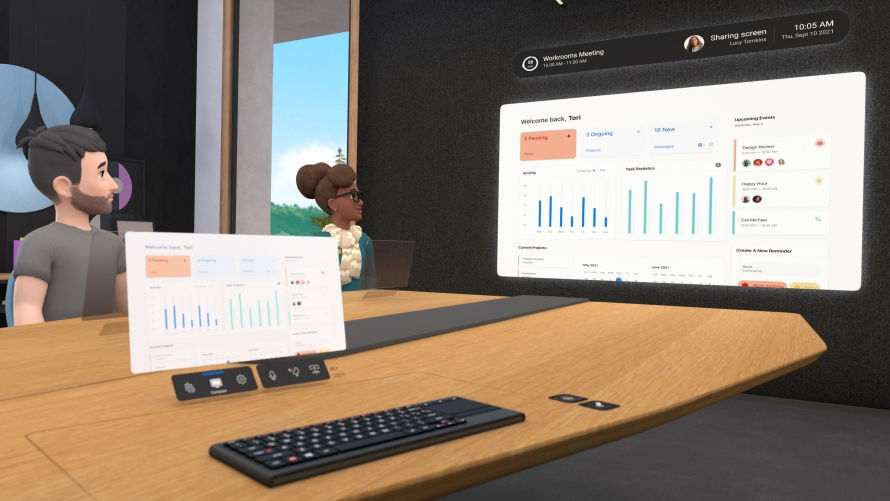
VR Will Play a Big Part in the Future of Work and May Help You Overcome a Fear of Presenting
Virtual Reality (VR) has slowly gained popularity over the past decade. Yet, it has not achieved the attraction many technology experts thought it would by now. There have been assumptions that the world or parts of it would be living out the book Ready Player One, spending most of our waking time going to work or school in the "metaverse." We are not quite there yet, the majority of us who are not into gaming don't see VR making much of an impact in our life.
However, Facebook (now “Meta”) is betting that VR will take off in the next couple of years, not in games but within the workforce, hinted at by their launch of Horizon Workrooms. In this VR conference room, participants can gather as if it were in person and even write or draw on virtual whiteboards. The results of the pandemic and the shift to remote and hybrid work, including the massive adoption of collaboration tools such as Microsoft Teams, has undoubtedly sped up the projection of VR in the workplace.
VR can also play a significant role in job-specific training, like customer service interactions. In this case, VR might simulate a conversation with a virtual customer to help agents learn to improve satisfaction. Ovation has even designed a VR simulator for individuals to overcome their fear of public speaking. This tool lets people practice presenting and provides a recorded version with feedback.
The Early Majority Phase of Web 3.0 and How to Earn Money From Your Personal Data
Move over tech monopolies, there's a big rumor that these "data-opolies" will start to decline as Web 3.0 changes the way users can control their data. Data is one of the main reasons the members of GAFAM (Google, Amazon, Facebook, Apple & Microsoft) came to be. Data they collected and owned paved the way for new products, advertising, and the sale of raw data. Since data has been termed the gold of this era, why do we give our personal data away so freely?
Startups like Brave, a new internet browser, are betting on a near-term trend of users looking to control their data, limit the personal what they send out, and possibly even profit from the data they agree to share. The best way to understand Web 3.0 is to start interacting with it and download one of the applications in the image below. In my experience, upon downloading Brave and playing around with it for less than 5 minutes, 370 trackers and ads were blocked, saving 18 seconds of my time. Rather than data or even money, time is the real currency. Brave and the wave of new Web 3.0 companies understand this. They are creating ways to help us monetize our time spent watching ads while protecting our personal data. Brave offers its own cryptocurrency called BAT (Brave Attention Tokens) that you collect when you choose to watch an advertisement.
Ethlance, the first job market platform of its kind, is built entirely on blockchain and uses only cryptocurrency for payments. So why would someone choose Ethlance over Upwork or Fiverr? Because of blockchain technologies, the platform can sustainably run with 0% service fees, giving the money straight to the freelancers without taking a hefty cut of the profit.
Cryptocurrency is Not a Fad, and it's Just NOW Beginning to Gain Momentum
If you can believe it, it was back in 2008 that Satoshi Nakamoto wrote his paper on Bitcoin. It wasn't really until 2015, with a cover story for the Economist, that it started to become an accepted currency with more than the early adopters. Around the same time, Ethereum launched with an initial coin offering raising $18 million.
By 2018 there were the lucky individuals who got in early and made a significant return on their investment, while the rest of the world held their purse strings, sure that cryptocurrency would crash and disappear. To this day, some believe that our great financial institutions were more secure because they are based on a gold standard, a system under which nearly all countries fixed the value of their currencies in terms of a specified amount of gold , which is not true today. When Gen Z single-handedly changed the rules of investing over a Reddit post, many of us became aware that even the dollar does not have any other value than our collective agreement of what it's worth.
Today Bitcoin is estimated at over $45,000 USD, and at its highest, it has been worth $68,000. This is just the beginning. Bitcoin could be worth millions by the mid 2100s, because, unlike US dollars which can be printed over time, there can only be a certain amount of Bitcoins mined. As per blockchain.com, the remaining supply of Bitcoins will be mined by February 2140.
So why is cryptocurrency only just reaching the beginning of its peak now? It is easier than it ever has to invest in. It is so easy that even your grandparents in the US can invest in it through their financial institutions. The big Canadian banks are slower to jump on the crypto wagon. However, Canadians interested in investing in cryptocurrencies can use companies like WealthSimple, even those who are brand new to investing.
The Era of Quantum Computing and Artificial SUPER Intelligence
When we look back on AI in the early 2020s, referred to as narrow AI (ANI), it will look highly primitive to what is coming. Even though AI has been around since the 1950s, we have barely scratched the surface of its capabilities. That is because of computing power, or lack thereof, to really enable AI. Now, with quantum computing, big data, and IoT, we can see AI reach intelligence levels equal to humans called Artificial General Intelligence (AGI).
To understand why quantum computing is so essential to the development of AI, Google developed a quantum computer that is about 158 million times faster than the world's fastest supercomputer. However, processing big data with quantum computing is very expensive, like many new technologies are. A general rule, Moore’s Law, can be applied to the relationship between computing power and its cost. It states that the number of transistors on a microchip doubles about every two years, though the cost of computers is halved. With Moore's Law in mind, the year we will have the ability to reach AGI will be 2045. Two years after that, we will be able to get Artificial Super Intelligence (ASI), where AI will surpass the intelligence of humans.
Liftoff of The Commercial Space Age
In 2020 the first non-government space vehicle entered our orbit, and it was in 2021 that the first-ever all-civilian space flight took place. These are significant leaps in the space industry that has been heavily guarded and regulated by governments. These historic events mark the dawn of the commercial space age. They will help accelerate discoveries and space technology previously hindered by bureaucracies.
There are tremendous benefits that will come out of the commercial space age, including programs like Project Kuiper, a low Earth orbit satellite constellation that will provide fast, affordable broadband to unserved and underserved communities around the world. However, with this opportunity also comes great responsibility, and as humans, we must proceed cautiously. The more we launch into orbit, the more space waste we create. There are currently more than 3,000 dead satellites and up to 900,000 pieces of space junk floating around Earth. We must create a plan to minimize our footprint in space and create strict regulations on things like space mining, which could cause significant implications to the universe.
Sustainable Cloud Computing and Conscious Capitalism
As most cloud providers commit to reaching zero-net emissions by 2030, there is a growing concern about the environmental impact of computing. By 2040, the information and technology sector is expected to account for 14% of the world's carbon footprint. With technologies like Bitcoin, that carbon footprint percentage could double. In 2019, researchers at the University of Cambridge estimated that the energy needed to maintain the Bitcoin network surpassed that of the entire nation of Switzerland. Other blockchain technologies, such as Ethereum, are more environmentally friendly as Ethereum has no energy-intensive mining process.
Business leaders across the globe will continue to make conscious sustainability decisions around their carbon impact. Forbes states that environmental, social, and governance (ESG) agendas will become a strategic business component for this year. Customers and even employees will increasingly demand efforts towards sustainability and conscious capitalism.
If you are interested in learning more about building a strategy around sustainable cloud computing, Google's Energy Transition and Sustainability Lead, Trinity Lloyd, is presenting on February 10 on "transforming towards sustainability."









Comments